Horizon on Azure VMware Solution Configuration
This chapter is one of a series that make up the VMware Workspace ONE and VMware Horizon Reference Architecture, a framework that provides guidance on the architecture, design considerations, and deployment of VMware Workspace ONE® and VMware Horizon® solutions. This chapter provides information about common configuration and deployment tasks for VMware Horizon on Azure VMware® Solution. A companion chapter, Horizon 8 on Azure VMware Solution Architecture, provides guidance on the architecture and design.
Deploying Horizon with Azure VMware Solution
This section covers specific information for deploying Horizon on Azure VMware Solution. It contains separate guidance on the two supported deployment architectures, which are explained in Deployment Options.
- All-in-SDDC Architecture - A consolidated design with all the Horizon components located inside each SDDC.
- Federated Architecture – A design where the Horizon management components are located in Azure and the Horizon resources (desktops and RDS Hosts for published applications) are located in the AVS SDDCs.
At a high level, the following steps are required to deploy Horizon with Azure VMware Solution:
- Create a Private Cloud. See the Azure VMware Solution documentation. The recommendation for a production environment is to use a minimum of three hosts in a cluster.
- Deploy Horizon 8 on the Azure VMware Solution, following the architecture described in Scaling Deployments.
- See the Horizon documentation and Horizon Installation and Configuration.
- See the VMware Knowledge Base article VMware Horizon on Azure VMware Solution (AVS) Support (80850) for features and versions supported on AVS.
- Set up the Horizon environment on Azure VMware Solution.
SDDC Creation
Create a Private Cloud. See the Azure VMware Solution documentation. The recommendation for a production environment is to use a minimum of three hosts in a cluster.
Gather SDDC Credentials
- Gather the VMware vCenter® and VMware NSX® URLs and credentials.
- In the Azure Portal, go to Azure VMware Solution.
- Go to your AVS Private cloud, then select VMware credentials under the Manage section of the middle menu.
- Copy the vCenter Web Client URL, vCenter admin user, vCenter admin password, VMware NSX-T™ Data Center Manager URL, NSX-T Manager admin user, and NSX-T Manager admin password.
All-in-SDDC Deployment
In an All-in-SDDC architecture deployment, all the Horizon components are located inside the Azure VMware Solution SDDC and run on vSphere. To prepare the SDDC, several tasks need to be completed before installing Horizon, including creating network segments and resource pools.
Create Network Segments
As covered in All-In-SDDC Architecture Networking, to allow for proper isolation of resources, several network segments need to be created inside the SDDC.
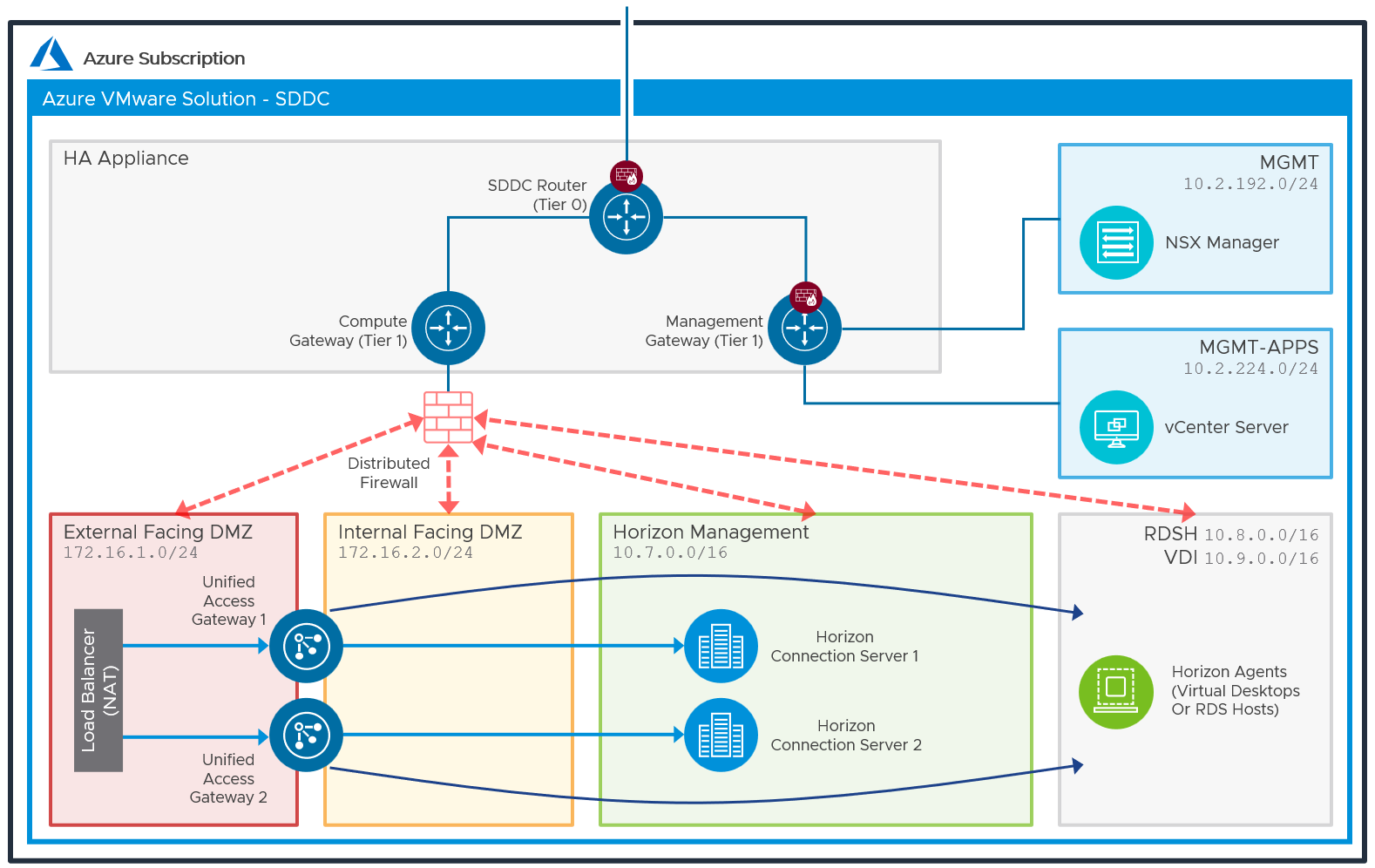
Figure 1: Network Diagram with All-In-SDDC Architecture (Subnets are for Illustrative Purposes Only)
Network segments can be added using the NSX-T admin console:
- Select the Networking tab.
- Using the left-hand menu, navigate to Connectivity > Segments.
- Under Segments, select Add Segment.
- Add segments for the following networks, defining a Segment Name and Subnet. The Type should be left as the default Routed.
- Add segments for External-DMZ, Internal-DMZ, Horizon-Management, VDI, and RDSH.
- For the VDI and RDSH segments, also launch and complete the Set DHCP Config wizard.
Create Resource Pools
Two vSphere resource groups are automatically created when the SDDC is created. It is recommended that the Compute-Resource Pool has child resource pools created in it to allow prioritization of the management servers and desktops/ RDS Hosts.
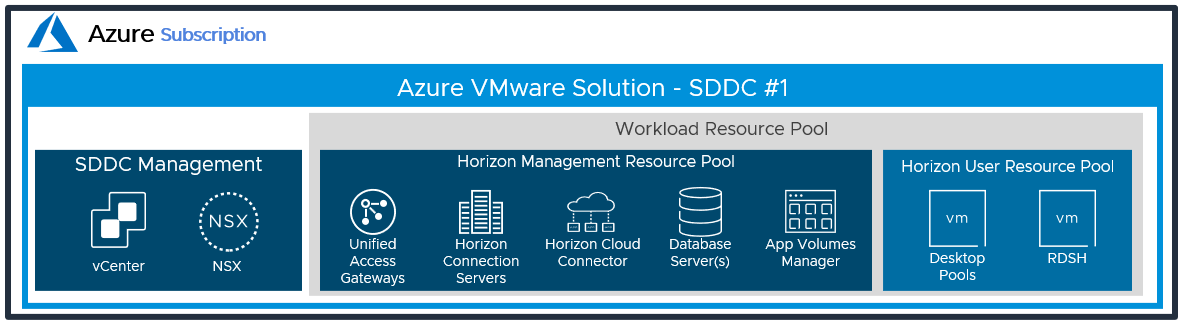
Figure 2: Resource Pools for All-in-SDDC Architecture of Horizon on Azure VMware Solution
In the vSphere Client:
- Click Menu and select Hosts and Clusters.
- Browse to and expand vCenter > SDDC-Datacenter > Cluster-1 > Compute-ResourcePool.
- Right-click and select New Resource Pool.
- Create two new resource pools for Horizon-Management and Horizon-User.
See Managing Resource Pools for more information.
Window Server Template
To facilitate the creation of Windows servers for the various Horizon management components, either import an existing vSphere VM template or create a new VM and convert it to a template.
- Upload VM template or Windows Server ISO.
- Import customization specifications.
All-in-SDCC Firewall Rules
The firewall service on Azure VMware Solution is based on NSX-T and provides both Distributed (Micro-segmentation) and Gateway Firewall Services.
To simplify the management of the Gateway Firewall, VMware recommends using Groups (located under Networking & Security -- Inventory).
- Pre-create groups for your on-premises vSphere management components, VDI components, and applications to be accessible from Azure.
- Do the same for VDI components deployed in the AVS SDDC. Groups for vSphere management components are already pre-created by VMware. While creating a group, you need to specify IP addresses using CIDR notation.
- You can include a single host as a member by specifying a /32 mask or a continuous range of IPs using relevant CIDR (such as /24 to include all IPs within a 24-bit subnet).
Note: Default behavior of both Management and Gateway Firewall is set to deny all traffic not explicitly enabled.
External Horizon Traffic
There are different options for providing inbound traffic in Azure. In this reference architecture implementation, a Virtual WAN secured hub with Azure Firewall, with L4 and DNAT, was used. There are other options available for allowing inbound traffic. See the External Access to All-in-SDDC Deployments section of All-In-SDDC Architecture Networking.
External Horizon sessions connect through the Unified Access Gateways (UAGs). In the deployment carried out for this reference architecture, the Unified Access Gateways (UAGs) were configured using high availability (HA). When using UAG high availability, n+1 public IP addresses are required:
- One IP address for the load-balanced floating virtual IP address (VIP) used for the XML-API
- An additional one per Unified Access Gateway appliance for the secondary Horizon protocol traffic (Blast, PCoIP, tunnel)
The required number of public IP addresses were configured in the Azure Firewall Manager Virtual Hub. External DNS records were created for each these.
Azure Firewall Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) rules were added to the Azure Firewall Policy to route and allow the required network ports from the public IP addresses to the UAG VIP and individual UAG appliances. To understand the required ports for Horizon, see Network Ports in Horizon.
Federated Deployment
In a federated architecture deployment, the Horizon management components are located in Azure.
Instance Types for Federated Deployment
The following table lists the Azure instances used based on a 2,000-desktop deployment example. Different Azure instance sizes can be used, although consideration should be given to the vCPU, memory, and expected network bandwidth available on the different instance sizes. This can have an impact on the number of sessions a management component can support. See Dsv4-series for details on other Azure instance sizes.
Table 1 gives example sizing for the server components that were used at the time of writing.
Table 1: Horizon Component Instance Types on Azure (Example)
| Horizon Infrastructure | Instance | vCPU | Memory | Amount |
| Connection Server | D4s_v4 | 4 | 16 | 1 per 4,000 sessions, +1 |
| Unified Access Gateway | D4s_v4 | 4 | 16 | 1 per 2,000* sessions, +1 |
| App Volumes Manager | D4s_v4 | 4 | 16 | 1 per 2,000 sessions, +1 |
| Horizon Cloud Connector | D8_v3 | 8 | 32 | 1 |
| Domain Controller* | D4s_v4 | 4 | 16 | Minimum 2 |
| MS-SQL Database* | D4s_v4 | 4 | 16 | Minimum 2 |
| Windows file share* | D4s_v4 | 4 | 16 | Minimum 2 |
*Size according to your environment
Connection Rules
Use the Azure portal to create an ExpressRoute in the vNet to connect to your on-premises management network. Finally, specify DNS server addresses for the management network.
Federated Firewall Rules
To set up a successful hybrid cloud deployment, you must follow these firewall rules. The following table describes firewall rules for the Azure vNet.
Table 2: Management Inbound Security Rules
| Rule Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action |
| Allow-UAG-CS-XML_API | 443 | TCP | Unified Access Gateway Internal - Application Security Group | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_443-CS | 443, 8443 | Any | Any | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_AVSDesktop-AVM | 443 | TCP | VDI Subnet | AppVolumes Managers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_DomainControllerInbound | Any | Any | Horizon Management Subnet, VDI Subnet, On-premises Management Subnet | Domain Controllers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_AVM-MGMT-DC | 443 | TCP | Horizon Management Subnet | AppVolumes Managers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_LDAP_Replication-CS-CS | 22389, 22636, 49152-65535, 389, 135, 32111, 4100,4101 | TCP | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_InterPODCommunication | 8472, 22389, 22636, 49152-65535, 135 | TCP | On-premises Management Subnet | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_CloudConnector-CS | 443, 4002 | TCP | Cloud Connector - Application Security Group | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_WorkspaceONEConnector-CS | 443, 389 | TCP | WS ONE Access Connector - Application Security Group | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_AVM-DB | 1433 | TCP | AppVolumes Managers - Application Security Group | SQL Database - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_AVSDesktop-CS | 4001,4002,389 | TCP | VDI Subnet | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_DFS_FileServerAccess | 135, 137, 138, 139, 445, 5445, 5722 | Any | Horizon Management Subnet, VDI Subnet, On-premises Management Subnet | File Server - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_UAG-DNSonDC | 53 | Any | Unified Access Gateway Internal - Application Security Group | Domain Controllers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_CloudConnectorMgmt | 443 | TCP | Horizon Management Subnet | Cloud Connector - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_ALB-AVM | 443 | TCP | AzureLoadBalancer | AppVolumes Managers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_ALB-CS | 443, 8443 | TCP | AzureLoadBalancer | Connection Servers - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Deny_All | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
| AllowVnetInBound | Any | Any | VirtualNetwork | VirtualNetwork | Allow |
| AllowAzureLoadBalancerInBound | Any | Any | AzureLoadBalancer | Any | Allow |
| DenyAllInBound | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
Table 3: Management and Internal DMZ Outbound Security Rules
| Rule Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action |
| AllowVnetOutBound | Any | Any | VirtualNetwork | VirtualNetwork | Allow |
| AllowInternetOutBound | Any | Any | Any | Internet | Allow |
| DenyAllOutBound | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
Table 4: Internal DMZ Inbound Security Rules
| Rule Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action |
| Allow_UAG-Management | 9443 | TCP | Horizon Management Subnet | Unified Access Gateway Internal - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Deny_All | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
| AllowVnetInBound | Any | Any | VirtualNetwork | VirtualNetwork | Allow |
| AllowAzureLoadBalancerInBound | Any | Any | AzureLoadBalancer | Any | Allow |
| DenyAllInBound | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
Table 5: External Inbound Security Rules
| Rule Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action |
| Port_443 | 443 | TCP | Any | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| BLAST_TCP | 8443 | TCP | Any | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| BLAST_UDP | 8443 | UDP | Any | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| UDP_Tunnel | 443 | UDP | Any | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| PCoIP_TCP | 4172 | TCP | Any | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| PCoIP_UDP | 4172 | UDP | Any | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| Allow_ALB-UAG-EXT | 443 | TCP | AzureLoadBalancer | Unified Access Gateway External - Application Security Group | Allow |
| AllowVnetInBound | Any | Any | VirtualNetwork | VirtualNetwork | Allow |
| AllowAzureLoadBalancerInBound | Any | Any | AzureLoadBalancer | Any | Allow |
| DenyAllInBound | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
Table 6: External DMZ Outbound Security Rules
| Rule Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action |
| AllowInternetOutBound | Any | Any | Any | Internet | Allow |
| DenyAllOutBound | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny |
Federated Load Balancers
For redundancy, load balancers are used for Unified Access Gateways, Connection Servers, and App Volumes Managers. In Azure, when adding a load balancer, outbound NAT is no longer working for internal load balancers. As such, every component behind a load balancer also gets connected to an outbound-only load balancer for Internet access. Internet access is useful for certificate revocation list checking and updates.
Table 7: Load Balancer Rules Settings
| Name | UAG | CS | AVM | Outbound Internet |
| SKU | Public Standard | Internal Standard | Internal Standard | Public Standard |
| Protocol | TCP | TCP | TCP | All |
| Port | 443 | 443 | 443 | N/A |
| Backend port | 443 | 443 | 443 | N/A |
| Backend Pool | Unified Access Gateways | Connection Servers | App Volumes Managers | Connection Servers, App Volumes Managers |
| Health Probe | HTTPS:443/favicon.ico | HTTPS:443/favicon.ico | HTTPS:443/health_check | N/A |
| Session Persistence | Client IP | Client IP | Client IP | N/A |
| Floating IP | Disabled | Disabled | Disabled | N/A |
| TCP reset | Disabled | Disabled | Disabled | N/A |
| SNAT | Use outbound rules | Use outbound rules | Use outbound rules | na |
Horizon Installation
When you set up the Horizon environment on Azure VMware Solution, you must install and configure the following components:
- Install Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, and KMS servers.
- Optionally, install RDS license servers.
- Install one or more Horizon Connector Servers. See Connection Server Deployment.
- Install one or more Unified Access Gateways. See Unified Access Gateway Deployment.
- Connect to Horizon Cloud Service using either the Horizon Edge Gateway or the Horizon Cloud Connector. See Connecting to Horizon Cloud Service.
Connection Server Deployment
With Horizon 8, when deploying the first Connection Server in the SDDC, make sure to choose Azure as the deployment type. This sets the proper configuration and permissions on the Connection Server and Virtual Center. This choice is only made on the first Connection Server in a pod.
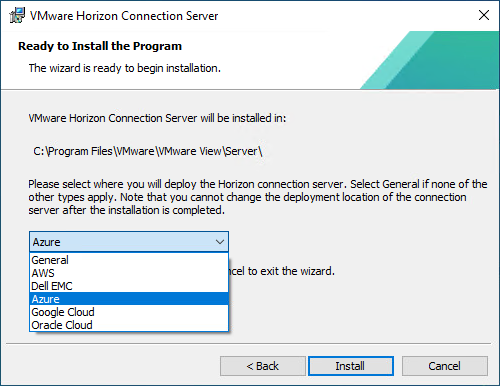
Figure 3: Horizon Connection Server Installation Platform Choice
- Version 8 2006 or later should be used.
- Optionally, install a Horizon event database on a Microsoft SQL Server.
Unified Access Gateway Deployment
Deploy Unified Access Gateway (UAG) appliances and connect them to the Connection Servers if your deployment supports external users.
- All-in-SDDC deployments - UAGs are deployed onto vSphere in the SDDC. Follow the documentation and instructions in Deploying and Configuring VMware Unified Access Gateway and the tutorial Deploying Unified Access Gateway on vSphere with Two NICs Through PowerShell.
- Federated deployments - UAGs are deployed into Microsoft Azure. Follow the documentation and instructions in Unified Access Gateway PowerShell Deployment to Microsoft Azure and the tutorial in Deploying Unified Access Gateway on Microsoft Azure.
Further deployment guidance can be found in Deployment Methods in the Unified Access Gateway Architecture chapter and in the Unified Access Gateway Activity Path.
General deployment guidance:
- Use Unified Access Gateway version 20.06 or later.
- Use the PowerShell script to include the password and encode special characters in the INI configuration file. For more information, see the Unified Access Gateway documentation.
- Specify static routes for the NIC connected to the Internal DMZ and specify the appropriate RFC1918 networks with the Internal DMZ gateway.
- For example: routes1=10.0.0.0/8 10.6.4.1,172.16.0.0/12 10.6.4.1,192.168.0.0/16 10.6.4.1
- Where: 10.6.4.1 is the Internal DMZ gateway.
Connecting to Horizon Cloud Service
There are currently two versions of Horizon Cloud Service. Depending on which you intend to connect the Horizon pod to, you will need to deploy the corresponding connector appliance, one per Horizon pod.
- Horizon Cloud Service - next-gen uses the Horizon Edge Gateway.
- First-gen Horizon Cloud Service uses the Horizon Cloud Connector.
Horizon Edge Gateway Deployment
To connect to the Horizon Cloud Service - next-gen, one Horizon Edge Gateway appliance is deployed per Horizon Pod. See the following documentation resources to assist in the Horizon Edge Gateway deployment:
- VMware Horizon Cloud Service - next-gen Deployment and Onboarding
- Requirements Checklist for Deploying a Horizon 8 Edge
- Horizon 8 Deployments, Horizon Edge - Preparing to Deploy
- Deploying a Horizon 8 Edge for Use with Horizon 8 Deployments and the Horizon Cloud - next-gen Control Plane
Horizon Cloud Connector Deployment
To connect to the first-gen Horizon Cloud Service, one Horizon Cloud Connector is deployed per Horizon Pod. For more information, see Onboarding a Horizon Pod to Horizon Cloud Control Plane.
For the latest guidance on sizing the Horizon Cloud Connector when deploying on AVS, see VMware Horizon Pods with Horizon Cloud Control Plane - Requirements Checklist.
Deploying Horizon over Hybrid Cloud
You might already have Horizon environments on-premises or on another cloud platform. The Horizon pod on-premises and your Horizon pod with Azure VMware Solution can be managed separately. Alternatively, you can extend your other Horizon environments by linking them with your Horizon with Azure VMware Solution environment using Cloud Pod Architecture (CPA). Deploying your Horizon environment over a hybrid cloud enables you to manage your on-premises deployment and your cloud deployment in a single federated space.
For hybrid cloud deployment, follow these steps.
- Configure ExpressRoute and firewall rules to enable the Connection Server instance with Azure VMware Solution to communicate with the Connection Server instance on-premises.
- Prepare Microsoft Active Directory (AD) and choose to set up a one-way trust or a two-way trust.
- Ensure that your on-premises Horizon version is 7.5 or later.
Note: The Horizon version deployed on-premises does not have to match the Horizon version deployed on Azure VMware Solution. However, you cannot mix a Horizon 7.4 pod (or earlier) with a Horizon 8 or 7 pod within the same CPA. - Use Cloud Pod Architecture to connect the other Horizon pods against the Horizon pod with Azure VMware Solution.
- For easy sharing of VM images and ISO images, you can use the vCenter Content Library on each vCenter Server.
Summary and Additional Resources
Now that you have come to the end of this configuration chapter on Horizon on Azure VMware Solution, you can return to the landing page and use the tabs, search, or scroll to select your next chapter in one of the following sections:
- Overview chapters provide understanding of business drivers, use cases, and service definitions.
- Architecture chapters give design guidance on the products you are interested in including in your platform, including Workspace ONE UEM, Workspace ONE Access, Workspace ONE Assist, Workspace ONE Intelligence, Horizon Cloud Service, Horizon, App Volumes, Dynamic Environment Manager, and Unified Access Gateway.
- Integration chapters cover the integration of products, components, and services you need to create the platform capable of delivering the services that you want to deliver to your users.
- Configuration chapters provide reference for specific tasks as you build your platform, such as installation, deployment, and configuration processes for Workspace ONE, Horizon Cloud Service, Horizon, App Volumes, Dynamic Environment Management, and more.
Additional Resources
For more information about VMware Horizon on Azure VMware Solution, you can explore the following resources:
- Azure VMware Solution product page
- Tech Zone Azure VMware Solution landing page
- VMware Horizon on Azure VMware Solution documentation
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| 2023-07-25 |
|
| 2023-04-20 |
|
Author and Contributors
This chapter was written by:
- Hilko Lantinga is a Staff Engineer 2 in EUC R&D, VMware.
- Graeme Gordon is a Senior Staff End-User-Computing (EUC) Architect in End-User-Computing Technical Marketing, VMware.
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact VMware End-User-Computing Technical Marketing at euc_tech_content_feedback@vmware.com.
